Specify settings for WMA format to convert with help of Protected Music Converter.
When you select WMA output format and press Custom profile... button in Output format section on main program window, you will get dialog window shown below. By changing various WMA format settings in this dialog you can create your custom profile, which can be saved and used to set up conversions in Batch List later.
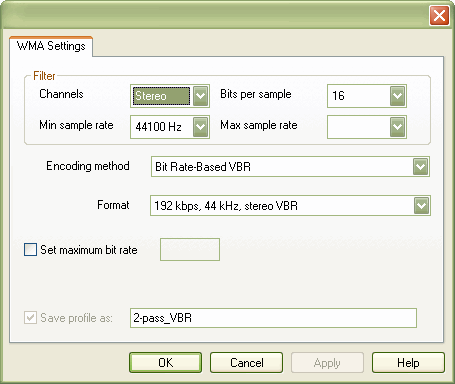
Filter
There are a lot of format variations for each encoding method in WMA codec and sometimes it's really hard to scroll through all available formats to find one you need. Group of controls on top of this dialog window helps you to set up restrictions to decrease number of formats shown. (only formats matching restrictions will be shown)
- Channels
Here you can set restriction on number of channels supported in codec format, available options are: Mono, 2 Channels (Stereo), 5.1 Channels and 7.1 Channels. Only those formats which support given number of channels will be displayed in Format list.
- Bits per sample
Here you can set restriction on number of bits per sample supported in codec format, available options are: 16 bits per sample and 24 bits per sample. Only those formats which support given number of bits per sample will be displayed in Format list.
- Min sample rate
Here you can set restriction on sample rate supported in codec format, available options are: 8000Hz, 11025Hz, 16000Hz, 22050Hz, 32000Hz, 44100Hz, 48000Hz, 88200Hz and 96000Hz. Only those formats which support sample rate equal or greater than given value will be displayed in Format list.
- Max sample rate
Here you can set restriction on sample rate supported in codec format, available options are: 8000Hz, 11025Hz, 16000Hz, 22050Hz, 32000Hz, 44100Hz, 48000Hz, 88200Hz and 96000Hz. Only those formats which support sample rate equal or less than given value will be displayed in Format list.
Encoding method.
There are five encoding methods available in WMA audio format:
- 1-pass Constant Bit Rate (CBR)
The main advantage of CBR encoding is that the bit rate and size of the encoded stream are known prior to encoding. For example, if you are encoding a three minute song at 32,000 bits per second, you know that the file size will be about 704 kilobytes (32,000 bps x 180 seconds / 8 bits per byte / 1,024). You also know that the bandwidth required to stream the encoded content is about 32,000 bits per second.
The disadvantage of CBR encoding is that the quality of the encoded content will not be constant. Because some content is more difficult to compress than others, parts of a CBR stream will be of lower quality than others.
CBR encoding will also result in inconsistent quality from one file to the next. If you use CBR to encode several songs of different genres at the same bit rate, you will probably notice some difference in the level of quality
In general, variations in the quality of a CBR file will be more pronounced at lower bit rates. At higher bit rates, the quality of a CBR encoded file will still vary, but the quality issues will be less noticeable to the user. When using CBR encoding, you should set the bandwidth as high as your delivery scenario allows.
- 2-pass CBR
When you use two-pass encoding, the codec processes all of the samples for the stream twice. On the first pass, the codec gathers information about the content of the stream. On the second pass, the codec uses the information gathered on the first pass to optimize the encoding process for the stream.
In the CBR encoding mode, files that are encoded in two passes are generally more efficient than files encoded in a single pass. - Quality based Variable Bit Rate (VBR)
The first type of VBR encoding is quality-based, which uses one encoding pass. Quality based VBR encoding enables you to specify a level of quality for a digital media stream instead of a bit rate. The codec will then encode the content so that all samples are of comparable quality.
The main advantage of quality-based VBR encoding is that quality is consistent within a file and from one file to the next. For example, you can write a program to copy songs from CD to ASF files on a computer. In this case, consistent quality is probably more important to the end-user experience than consistent file size. Using quality-based VBR encoding would ensure that all of the songs copied are of the same quality.
The disadvantage of quality-based VBR encoding is that there is really no way to know the size or bandwidth requirements of the encoded media before encoding. This can make quality-based VBR-encoded files inappropriate for circumstances where memory or bandwidth are restricted, such as portable media players, or low-bandwidth Internet connections.
In general, quality-based VBR encoding is well suited for local playback or high bandwidth network connections. In those cases, the consistent quality will provide a better user experience.
- Bit rate based VBR
When you use two-pass encoding, the codec will process all of the samples for the stream twice. On the first pass, the codec gathers information about the content of the stream. On the second pass, the codec uses the information gathered on the first pass to optimize the encoding process for the stream.
When using 2-pass VBR encoding, you specify a bit rate for the stream, as you would with CBR encoding. Unlike CBR, however, the codec will use this value as the average bit rate for the stream and will encode so that the quality is as high as possible while maintaining the average. The actual bit rate at any point in the encoded stream can vary greatly from the average value.
In general, files that are encoded in two passes are much more efficient than files encoded in a single pass. The advantage of 2-pass VBR encoding is that the compressed stream will have the highest possible quality while staying within a predictable average bandwidth.
- Lossless VBR
This type of conversion compress audio content without quality loss, it means that audio content decompressed from Lossless audio is mathematically identical to original.
Lossless audio, in such a way, is useful for audio CD collection backup, but such a backup may take a lot of your hard drive space.
Set maximum bitrate
Here you can set restriction for maximum bit rate value, only available if you are using Bit rate based VBR encoding method.
Save profile as:
Here you can write down name for your new profile. When you are done with this dialog, press "OK" button and this set of options will be saved with given name for future use.
 Related Topics: OGG Vorbis custom profile
WAV custom profile
MP3 custom profile
Related Topics: OGG Vorbis custom profile
WAV custom profile
MP3 custom profile
Copyright © 2002-2024 LitexMedia